What is Prostate?
What Does It Do?
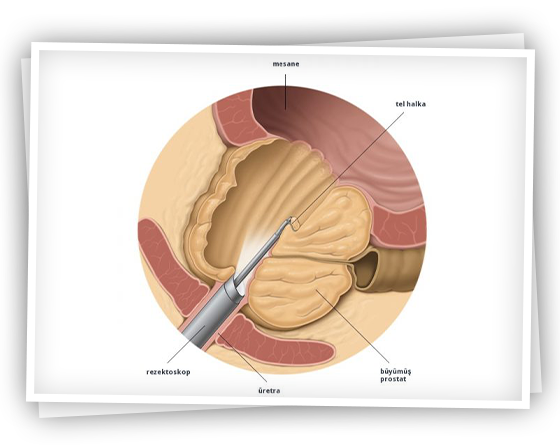
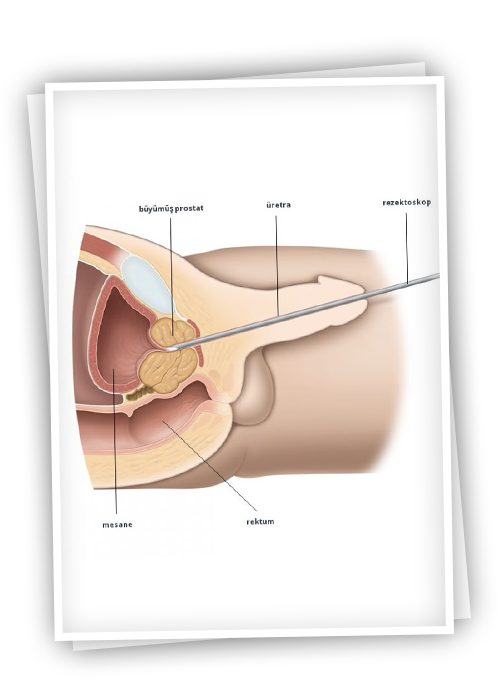
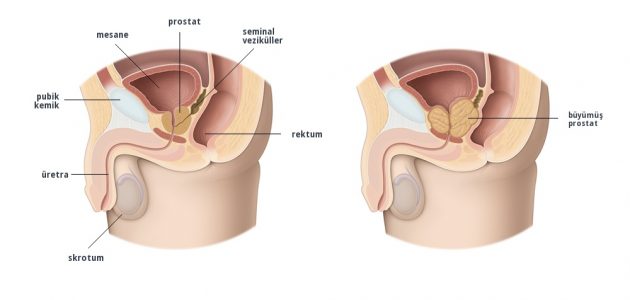
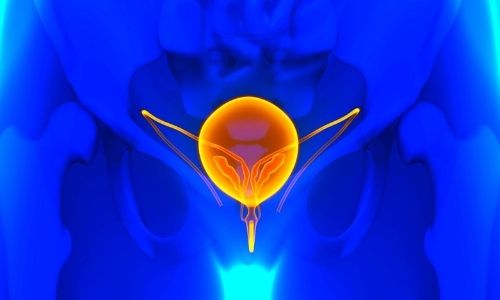
The prostate is a gland found in the urethra, below the bladder (bladder) and in men that surrounds the urethra (urethra). It is an organ that secretes 20-25 gr chestnut-shaped fluids found in the semen (semen).
As a result of hormonal changes in advancing age, the prostate gland begins to grow and narrows the urinary tract, causing complaints. Prostate enlargement is mostly in the form of benign prostate enlargement. Benign prostate enlargements should be differentiated from prostate cancers.
















thank you for sharing information About Prostate its really helpful for the reader.