What Causes Chronic Cystitis & Interstitial Cystitis?
The structure of the female genital organs plays a facilitating role for infections. The short external urethra (urethra) is located close to the anal region. The most common factor detected in the urine cultures of patients with cystitis is the bacteria found in the stool (Escherichia coli-coli bacillus). Bacteria in the anal area usually settle in the urinary tract under unsuitable hygiene conditions and cause cystitis.
Cystitis is generally caused by a bacterial infection. The bacterium responsible for this disease is often called E.coli bacteria and causes an infection of the lower urinary tract. Apart from this, there are different types of cystitis that develop.
Interstitial cystitis is known as painful bladder syndrome and refers to the condition of chronic cystitis. The underlying cause of this disease cannot be determined exactly. Interstitial cystitis, which is difficult to diagnose and treat, develops with inflammation of the bladder surface epithelium.
This causes a feeling of discomfort, burning and severe pain. In addition, complaints of cystitis during urination continue for a long time.
Other causes of the disease include:
- Genetic factors
- Damage to the protective layer (epithelium) covering the bladder
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Presence of irritants in the urine
- Allergic reactions
- Damage to bladder nerves
Who Is It Commonly Seen?
Cystitis is usually seen in women. Its frequency increases especially in the sexually active period, honeymoon period, and post-menopausal period.
Does it flow?
Especially in young women, cystitis may be accompanied by sexually transmitted genital organ infections (vaginitis, cervicitis, PID). In these cases, discharge is accompanied by high fever, burning, a feeling of fullness. Sometimes an existing sexually transmitted disease mimics cystitis and patients apply to a urologist. In these cases, it would be a more correct approach to follow up and treat the patient with a gynecologist.
Is it transmitted by sexual intercourse?
It is not a sexually transmitted condition, but it is thought to be transmitted by the opposite sex because it occurs after sexual intercourse.
What are the Prevention Methods?
Women who have had cystitis should pay particular attention to the hygiene of the genital area. It is especially recommended to take a shower before and after sexual intercourse, to urinate after intercourse without waiting, to consume 2 liters of liquid per day, to wear cotton underwear and to change it frequently, and not to be constipated.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of cystitis is made based on the patient's complaints, examination findings and laboratory results. Urinalysis as a laboratory analysis is often sufficient in simple cystitis cases. Urine culture and antibiogram test are performed in complicated and frequently recurring patients. Urine culture identifies the bacterium that causes cystitis and shows which antibiotics this bacterium is sensitive to.
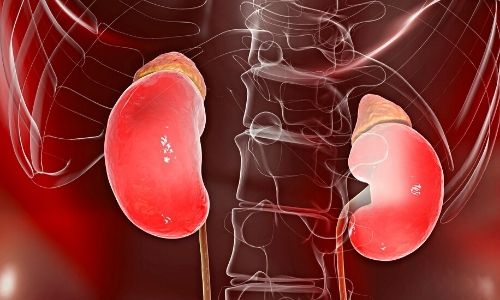
In kidney infections (pyelonephritis) accompanied by high fever and flank pain, urinary tract obstruction or stones should be investigated by ultrasonography or tomography.
Chronic Cystitis & Interstitial Diagnosis and Treatment Methods
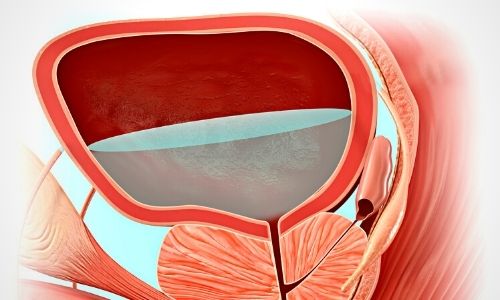
Interstitial cystitis is a problem that negatively affects daily life and can lead to more serious complications if left untreated. The disease causes thickening of the bladder wall over time and consequently less urine storage ability.
Due to the frequent need for urine, social life and quality of life decrease, and depression and stress are also observed in the patient. There are also problems in sexual life. Therefore, it is extremely important to treat the disease as soon as possible.
First of all, the disease must be diagnosed definitively. Because interstitial cystitis; It shows similar symptoms with diseases such as kidney stones, some sexual diseases, urinary tract infections, bladder cancer and endometriosis. Various diagnostic methods should be applied to exclude these diseases.
These include blood and urine tests. In addition, a detailed history covering the daily urination routine is listened from the patient, and the bladder and urinary tract are examined with a special device called cystoscopy. If the patient has pain and complaints for more than 6 months, interstitial cystitis is suspected. Other diagnostic methods applied are:
- Biopsy; tissue sample from the body
- Urine cytology; detection of cancerous cells in urine sample
If interstitial (chronic) cystitis is diagnosed at the end of these methods, treatment methods can be started. The priority in treatment is to improve the quality of life and eliminate existing complaints. Depending on the course of the disease and the severity of pain, more than one treatment method can be applied together in patients. Some patients may require additional surgical intervention. Age, health status, course of the disease, past diseases, drug sensitivity and many similar conditions are involved in the surgical operation. The main treatment methods are:
- Physical Therapy: Under the control of a physical therapist, movements for the development of pelvic muscles are performed and it is aimed to eliminate muscle abnormalities.
- Medication: Various muscle relaxants, pain relievers and steroids can be used to reduce pain and burning sensation during urination.
- Electrical Nerve Stimulation: Electrical stimulation, which strengthens the muscles that control the bladder and increases blood flow, can be done with a device placed in the abdomen or with physical therapy.
In addition, some changes in living standards also play a major role in treatment. These include gaining healthy eating habits, stopping alcohol and smoking, and limiting consumption of chocolate and spicy foods.
In the event that all these do not work, the patient undergoes surgery. For this, enlargement of the bladder, burning the damaged structures in it and similar options are evaluated.
In this process, it is very important to listen to the advice and recommendations of the specialist doctor. In order to eliminate the problem, the doctor and the patient should decide together in the treatment application.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of cystitis is antibiotic therapy. Short-term or single-dose antibiotics are used in the treatment of simple cystitis. Antibiotics that are effective against the microbes grown in the urine culture are preferred in cystitis that does not respond to treatment.

















Thank you for sharing useful information. It is really a great blog about Interstitial Cystitis .
Great information about cystitis. it’s really helpful for the Reader.